Principal, Dodd Kattman, has been named a 2024 Design Champion in Environments for Aging's national awards competition.

In recent years, Ambulatory Surgery Centers (ASCs) have become an increasingly popular solution for providers due to the affordable cost (often in response to shifting reimbursement rates), ability to embrace specialization, and convenience to patients. Popular types of procedures offered within an ASC often range from orthopedic and endoscopy to pain management and neurology. These specialized facilities absorb volume from hospital-based outpatient departments to provide efficient care for procedures that don’t require extended in-patient stays. The expansion of technologies suggests that ASCs will continue to increase the amount and type of outpatient care they can provide. By alleviating hospitals of cases that do not require inpatient care, ASCs can improve the efficiency and quality of care within communities. As healthcare technology continues to improve, the longevity of ASCs can depend on a number of variables. However, a key consideration relates to the right-sizing of the facility with a flexible and human-focused approach.
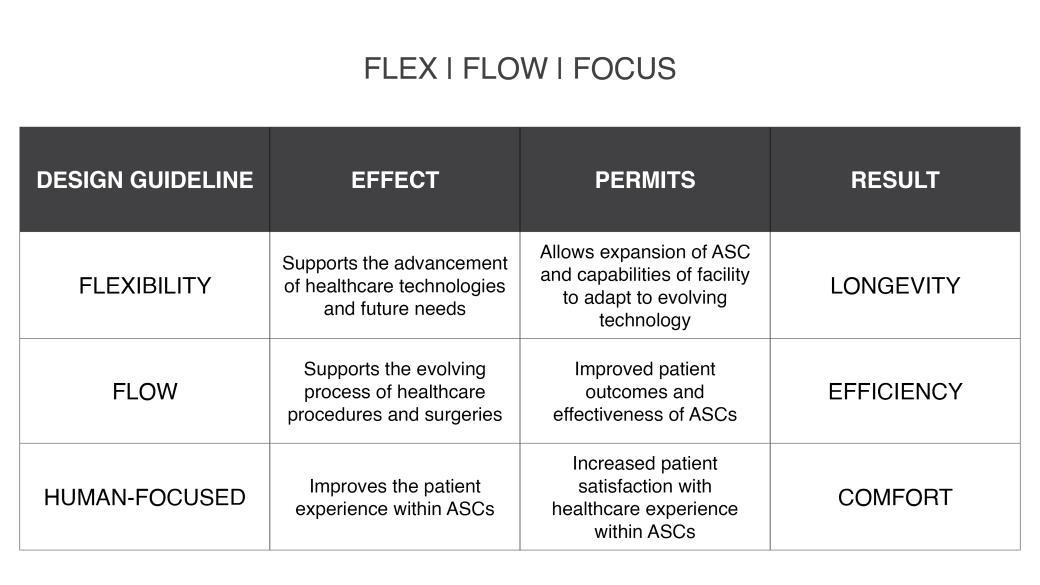
Flexibility
Flexibility has various implications in the development of an ASC, especially as it relates to the growing number of surgeries that can be performed in an outpatient setting. In supporting the diversity of surgical operations performed within today’s ASCs, flexibility prioritizes facilities that can achieve multiple functions without changing the whole system.
Flexibility can be expressed through various design principles. As defined by Steelcase Health, an international furniture solutions company, flexibility can be executed in four dimensions: versatility, modifiability, convertibility, and scalability. A flexible design might serve multiple functions by implementing modular and adjustable elements within the key clinical spaces.
Flexibility can also occur under more permanent circumstances. Some procedures may require spaces with specific needs to deliver the best quality of care. Despite current specific needs, the buildings’ success may rely on its ability to be easily renovated for other purposes in the future.
Key considerations include:
- Flexible surgical spaces that accommodate different types of procedures for multiple specialties.
- Flexible structures that can facilitate future expansion of ASCs to grow the clinical practice as technology advances.
- Clinical spaces with flexible functions such as a patient bay that serves as both a surgery prep and recovery space.
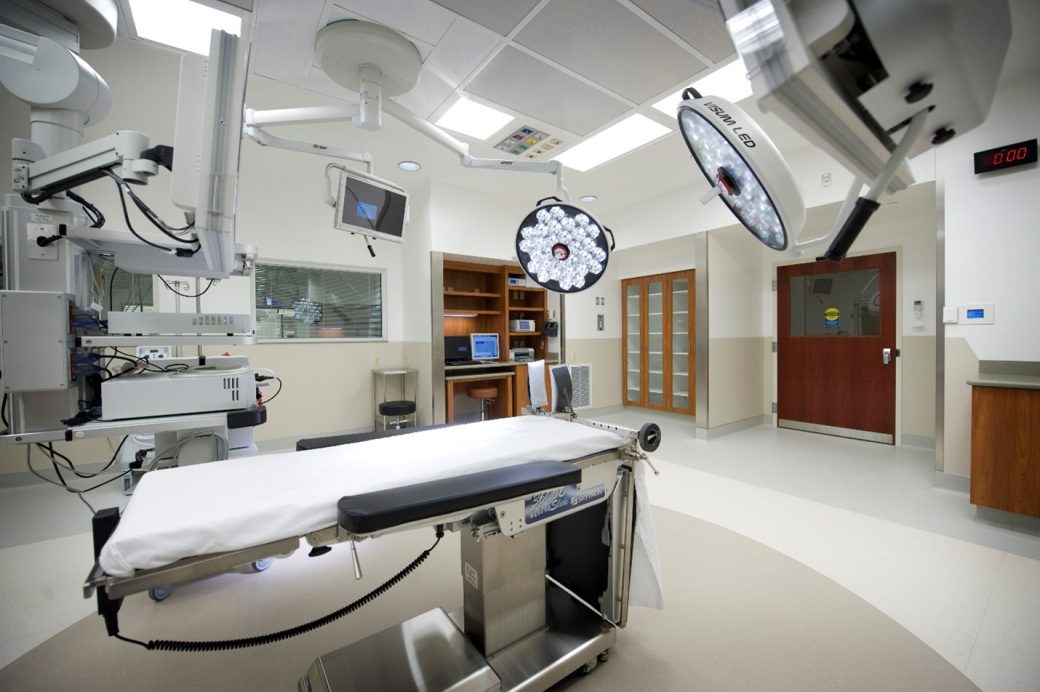
Ortho Northeast SurgeryONE | Fort Wayne, IN
Flow
One primary motivation for the development of ASCs is their intended convenience compared to larger hospital facilities. The efficiency and reliability of ASCs depends significantly on effective patient and staff flow. This is often a result of the circulation of patients, staff, family members, caregivers, and medical equipment. Each of these groups follow a unique path through the care experience. Making design decisions that consider the overlapping flow of these components within an ASC is critical to their success.
Design guidelines that improve flow within an ASC may include centralized patient support areas that minimize footsteps and can be accessed from multiple spaces, one-way circulation for patient carts in areas where appropriate, and the well-planned arrangement of materials and spaces to streamline the execution of care.
The arrangement of flexible spaces within an ASC can complement the flow of people and materials between them. Thoughtful considerations about the clinical workflow of the procedures being performed in a particular ASC can streamline services and improve the efficiency of care.
Key considerations include:
- Strategic one-way circulation for patient carts.
- Arrangement of spaces to streamline staff operations and workflow.
- Dual access storage cabinets to minimize the distance staff needs to travel for supplies.

Human Focused
A third and equally important consideration when designing an ASC is a human-focused approach. While flexibility and flow prioritize healthcare technology and procedures, a human-focused approach to design prioritizes people. This accounts for all people existing in the ASC for any given time. Patients, staff, owners, and caregivers all need to be considered in the designed elements of an ASC and the design should support people of all ages and abilities. Understanding the circumstances in which people visit ASCs should influence the importance of the comfort of the space. These design observations vary from facility to facility depending on the type of outpatient services they provide or if their patient population skews towards a particular age group.
Design guidelines that are human-focused may include clear signage, controllable lighting and temperature, privacy, reduced noise levels, access to the natural environment, safety and security, and children’s play areas. Human-focused design principles improve comfort and compatibility between people and the ASC facility.
Key considerations include:
- Make it local; understand and address the culture and needs of the immediate community.
- Maximize design features to increase patient comfort and satisfaction, clear and cohesive signage, controllable lighting, reduced noise levels, access to the natural environment, etc.
- Design decisions are made to benefit the patients, family members, staff, and owner.
ASCs are pivotal in managing the influx of healthcare demands throughout the nation. Their ability to mitigate needs and provide respective options for receiving more affordable care is promising. ASC developments offer a sustainable and growing opportunity to alleviate healthcare needs as the continuum of surgical procedures and technological advancements continue to evolve. Designing these facilities with flexible strategies that optimize flow and increase overall satisfaction with healthcare is essential to their contribution to the current and future scope of care.